For cars, buses, and other passenger vehicles to transport people and goods from Point A to B, they need to run with engines powered by different types of fuels.
An engine is a mechanical device that takes a combustible fuel (such as petroleum, diesel, liquified gas, natural gas, hydrogen or biofuel) and burns/combusts it to make mechanical parts move, ultimately causing a transmission to turn and a vehicle’s wheels to turn. In every day life, engines are classified based on the fuel they use as an energy source which is why we often compare the two most common types of fuels in Australia – diesel engines, or petrol engines.
For today’s guide, you’ll discover more about petrol and diesel engines—how both are similar or different in some ways.
What is a Petrol Engine?
A petrol engine, also known as a gasoline engine in parts of the world, belongs under the category of internal combustion engines. They are commonly used in vehicles like cars, motorcycles, machines, and others.
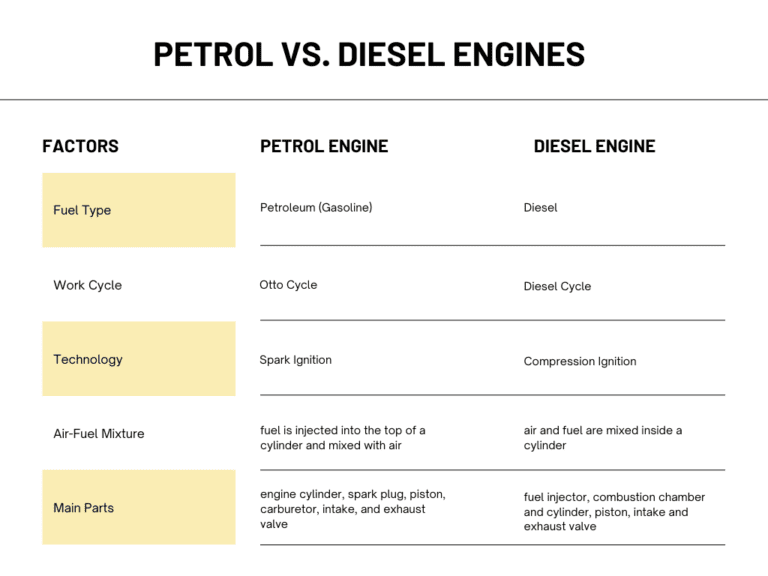
Petrol engines mix air and the fuel (in this case, petroleum) and uses a fuel injector to place this fuel on top of a piston that sits in a cylinder. When the engine is ready, it uses a spark plug to create a small spark and ignite the fuel, ultimately forcing the cylinder down a piston and creating movement. It runs on what is known as the Otto cycle (named after its inventor).
This process happens in a certain sequence (this depends on the number of cylinders that are in an engine and how it is configured) and the engine repeats this sequence in a faster or slower pace based on how fast you wish for the engine to rev/how fast you wish the vehicle to go.
This is the case for the most commonly found petrol engine, known as a piston-and-cylinder engine. This is the industry’s common practice and is found on all Mercedes-Benz petrol-powered vehicles. There is also another type of petrol-powered engine called the rotary engine. This engine ignites fuel and air, but instead of pushing multiple pistons up and down a cylinder, it turns a three-sided “rotor” around a circular chamber to create the movement. This type of engine is usually found in Japanese vehicles, and was a typically used engine in the 1990s – 2000s for performance figures.


What is a Diesel Engine?
The diesel engine is another type of internal combustion engine (ICE). It is also known as a compression-ignition engine that runs on diesel. This means that it uses compression ignition to convert energy in diesel fuel into mechanical energy. Typically, diesel engines are used to power vehicles and heavy machinery.
The diesel engine functions on a diesel cycle. This cycle encompasses a continuous pressure process, two isentropic processes, and a constant volume process.
In diesel engines, the diesel fuel is injected into a combustion chamber, and then ignited by the high temperature of the compressed air in the chamber (not by a spark plug). Adiabatic compression causes the high temperature of the air. In diesel engines, however, only the air is compressed, not the fuel.


Petrol Engine vs. Diesel Engines
Petrol and diesel engines are somewhat similar as they are both types of internal combustion engines. Both are designed to transform the chemical energy in fuel into mechanical energy.
This mechanical energy moves the pistons in the engine’s cylinders, which are connected to a crankshaft. The pistons’ up-and-down motion—known as linear motion—generates the movement necessary to move the vehicle forward.
Both engine types follow a similar principle of converting fuel into mechanical energy through a series of controlled explosions or combustions. However, the stark difference lies in how these combustions take place.
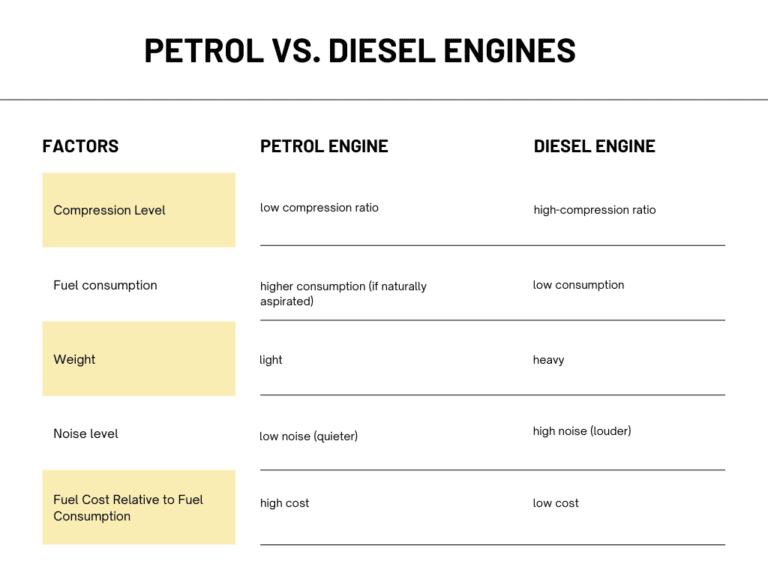
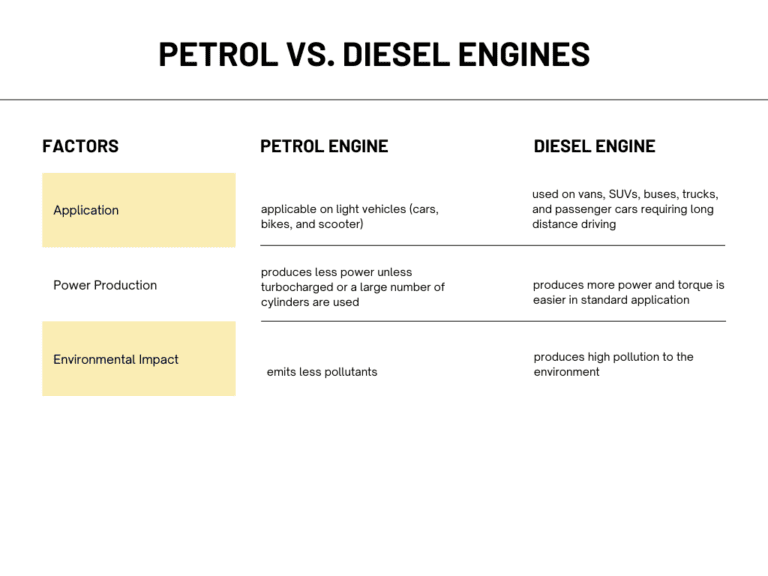
While petrol and diesel engines are similar because both are internal combustion engines, they have several differences that separate one from the other. The following table shows their differences.



Final Thoughts
Choosing between a petrol and diesel engine will depend on your specific needs, preferences, and the intended application. By considering factors such as fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, environmental impact, application, and maintenance requirements, you’re on your way to making an informed decision that resonates with your driving experience.
As a rule of thumb, petrol engines are more affordable, quieter, and more refined. On the other hand, diesel vehicles are a more durable and robust choice, have a longer lifecycle, and supply better fuel efficiency. Another notable benefit of going diesel is the fact that they can produce higher amounts of torque easily. Diesel-powered vehicles are usually cheaper to fill than petrol engines. Generally, diesel vehicles are more fuel-efficient than their gasoline counterparts due to their thicker density, higher compression ratio, and lower RPM performance.
Aside from better fuel economy, the diesel engine is built for heavy-duty driving—perfect for long drives and higher-mileage usage of a vehicle, carrying heavy cargo, and towing big loads. Since diesel engines last long, major engine overhauls or upgrades are often rare throughout the lifespan of a diesel vehicle.
If a diesel engine is the right choice for you, we recommend you work with diesel experts who can provide end-to-end routine maintenance and repairs for your Mercedes vehicle. At Eurostar Diesels, our passionate team of mechanics is well-trained in all aspects of the diesel engine and provides you with specialised services from oil changes to engine repair. Our service center locations in Hallam and Sunshine West are ready to serve you.
If you have more questions, feel free to contact us for all your Mercedes-Benz specialty solutions. Or better yet, book an appointment today for a one-on-one consultation with our experts.
